Highly available infrastructure
- Ability to obtain service, without experiencing components down.
- Minimizing access and thus the load, for example via caching.
- Adding redundancy to the system, ensuring failover to the good component.
Identity management
- Resolution of identities — users, groups, hosts, services, ...
- Verification of identities (authentication).
- Evaluation of access requests and attempts (authorization), based on centrally managed policies.
- For example:
ls -lon POSIX systems- It can make number of NSS (Name Service Switch) calls resolving owner and group identities.
- Identities can be stored on external identity source, not in
/etc.
FreeIPA
- Integration of multiple identity-management tools.
- directory server (LDAP), Kerberos key distribution center, one-time password (OTP) daemon
- optionally DNS server, certification authority, vault
- WebUI, command-line interface
- Built-in replication using 389 Directory Server replication functionality.
- Multi-master.
- Client machines get IPA-enrolled to one of the servers.
- Typically via
ipa-client-installwhich configures all subsystems.- Often using one-time password for the host identity.
- They can do a lot of caching.
- Typically via
IPA-enrolled systems
- SSSD (System Security Services Daemon):
- NSS service;
- PAM (Pluggable Authentication Module) service;
- plugs to other subsystems — sudo, Kerberos, ...
- DNS records can prioritize IPA servers used:
# /etc/sssd/sssd.conf [domain/example.com] ipa_server = _srv_, ipa1.example.com ...
- KDC's IP address cached in
/var/lib/sss/pubconf/kdcinfo.*.
FreeIPA replication
| IPA realm | ||||
| IPA server | ⇔ replication | IPA server | ||
| ↗ | ↑ | ↖ | ||
| IPA-enrolled system | IPA-enrolled system | IPA-enrolled system | ||
- IPA servers get found via DNS or with their hostname hardcoded on clients.
Replication and topology enhancements
Three areas of replication improvement:
- Replica promotion which simplifies setup of new replicas.
- Topology plugin for central control over replication agreements.
- DNS-based locations for central management of client priorities.
Replica promotion
- Promotion of any IPA-enrolled client to FreeIPA replica.
- Can also start with unenrolled host.
- GPG-encrypted replica information files no longer needed.
- The
ipa-replica-installtool still used. - Standard Kerberos authentication.
- With host OTP and
ipaservershost group, admin credentials do not need to be used on the replicas.
Example workflow
Create host record for the future replica, give the host ability to make itself a replica with the
ipaservershost group.
client$kinit adminPassword for admin@EXAMPLE.COM:client$ipa host-add replica.example.com --random----------------------------- Added host "replica.example.com" ----------------------------- Host name: replica.example.com Random password: ImgXN_VxNC,B Password: True Keytab: False Managed by: replica.example.comclient$ipa hostgroup-add-member ipaservers --hosts=replica.example.comHost-group: ipaservers Description: IPA server hosts Member hosts: master.example.com, replica.example.com ------------------------- Number of members added 1 -------------------------
Example workflow (cont)
On the replica machine:
replica#ipa-replica-install --password 'ImgXN_VxNC,B'Configuring client side components Client hostname: replica.example.com Realm: EXAMPLE.COM DNS Domain: example.com IPA Server: master.example.com...Enrolled in IPA realm EXAMPLE.COM Created /etc/ipa/default.conf...Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 1 minute...[28/43]: setting up initial replication Starting replication, please wait until this has completed. Update in progress, 6 seconds elapsed Update succeeded [29/43]: adding sasl mappings to the directory...[2/2]: configuring ipa-otpd to start on boot Done configuring ipa-otpd.
Replica promotion of IPA-enrolled client
- Check
/etc/ipa/default.confpoints to the master.[global] server = master.example.com xmlrpc_uri = https://master.example.com/ipa/xml
- After replica promotion, it gets updated to point to itself.
xmlrpc_uri = https://replica.example.com/ipa/xml
- Domain level at least 1 (important for upgrades).
ipa1# ipa domainlevel-get ----------------------- Current domain level: 1 -----------------------
Topology information
- Topology info is now replicated across all replicas.
ipa1$ipa topologysegment-find domain------------------ 3 segments matched ------------------ Segment name: ipa1.example.com-to-ipa2.example.com Left node: ipa1.example.com Right node: ipa2.example.com Connectivity: both Segment name: ipa2.example.com-to-ipa3.example.com Left node: ipa2.example.com Right node: ipa3.example.com Connectivity: both Segment name: ipa2.example.com-to-ipa4.example.com Left node: ipa2.example.com Right node: ipa4.example.com Connectivity: both ---------------------------- Number of entries returned 3
Topology graph
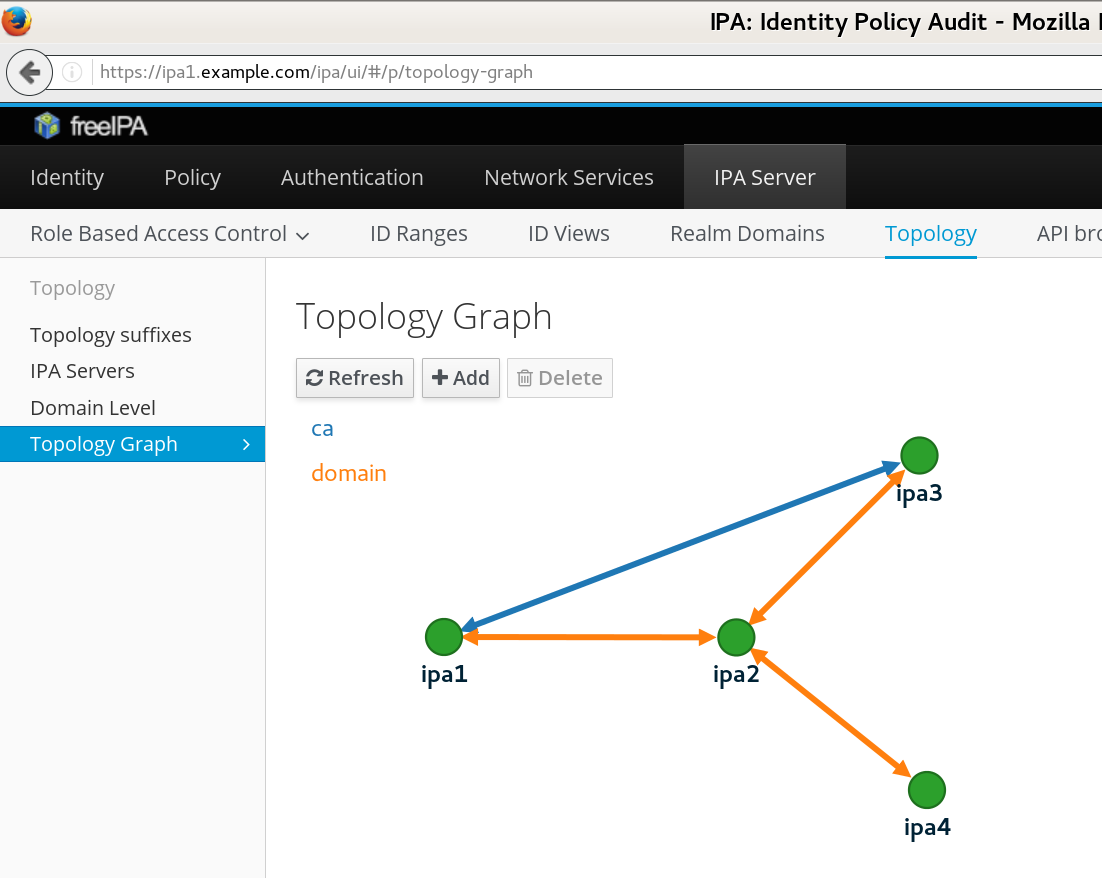 |
Managing topology
- Segment is added by creating it in directory server.
ipa1$ipa topologysegment-add domain ipa3.example.com-to-ipa4.example.com \ --leftnode=ipa3.example.com --rightnode=ipa4.example.com------------------------------------------------------ Added segment "ipa3.example.com-to-ipa4.example.com" ------------------------------------------------------ Segment name: ipa3.example.com-to-ipa4.example.com Left node: ipa3.example.com Right node: ipa4.example.com Connectivity: both
- Via command-line or WebUI.
- Information gets replicated to the target nodes.
- New replication agreement is established.
- The
casuffix is used for the certification authority. - Can only add segment between nodes that already have the role installed and configured.
DNS-based locations
- With easy way to set up replicas and segments, complex network topologies are possible.
- Clients should be able to seamlessly fail over.
- With DNS SRV records, no need to hardcode a particular FreeIPA server on clients.
- But different clients need different servers resolved, for “cheapest” operation.
- Traditionally, mix of hardcoded and SRV was used:
[domain/example.com] ipa_server = ipa1.example.com, _srv_
- Problem: configuration on every client.
- New DNS-based location feature allows grouping of FreeIPA servers and managing their priorities.
DNS-based locations operation
- FreeIPA server with embedded DNS server running in every location.
- Clients are configured to use that DNS server.
- E.g. via DHCP in given subnet — handled outside of FreeIPA.
- Can also resolve through that DNS server recursively.
- Locations defined, FreeIPA servers assigned to them.
- The DNS servers in each location will autogenerate SRV records as CNAMEs to given location.
Location definition
$ipa location-show emeaLocation name: emea Servers: ipa1.uk.example.com, ipa2.uk.example.com Advertised by servers: ipa1.uk.example.com, ipa2.uk.example.com Servers details: Server name: ipa1.uk.example.com Service weight: 10 Service relative weight: 25.0% Enabled server roles: CA server, DNS server, NTP server Server name: ipa2.uk.example.com Service weight: 30 Service relative weight: 75.0% Enabled server roles: DNS server, NTP server$ipa location-show usLocation name: us Servers: ipa1.houston.example.com Advertised by servers: ipa1.houston.example.com Servers details: Server name: ipa1.houston.example.com Service weight: 10 Service relative weight: 100.0% Enabled server roles: CA server, DNS server, NTP server
Location resolution
$dig +short @ipa1.uk.example.com. _kerberos._tcp.example.com SRV_kerberos._tcp.emea._locations.example.com. 0 10 88 ipa1.uk.example.com. 0 30 88 ipa2.uk.example.com. 50 10 88 ipa1.houston.example.com.$dig +short @ipa1.houston.example.com. _kerberos._tcp.example.com SRV_kerberos._tcp.us._locations.example.com. 50 10 88 ipa1.uk.example.com. 0 10 88 ipa1.houston.example.com. 50 30 88 ipa2.uk.example.com.
- Only SRV configuration is needed on clients.
[domain/example.com] ipa_server = _srv_
- Works for any service which can resolve SRV, not just SSSD.
- No more hardcoding server names on clients.
- Ideal for roaming clients (laptops).
Conclusion
- Replicas can be created in more automated manner.
- No admin password needed on the replica machine.
- No manual action needed on the master.
- Replication topology information is now replicated.
- It is possible to manage segments without having direct network connection to the nodes.
- Partitioning servers to locations removes need for hardcoding server names on clients for priority purposes.
References
- http://www.freeipa.org/page/V4/Replica_Promotion
- http://www.freeipa.org/page/V4/Manage_replication_topology
- http://www.freeipa.org/page/V4/DNS_Location_Mechanism

