Managing sudo rules for Fedora Atomic Host
2016-05-14
Abstract
SSSD provides identity, authentication, and authorization
services to the operating system and applications. On Fedora
Atomic Host, it is possible to run SSSD in a container,
using the fedora/sssd container image.
With FreeIPA/IdM (IPA) server, sudo rules can be
defined and managed and starting with Fedora Atomic 23.53,
they are observed.
SSSD on Atomic
As introduced in SSSD in container on Fedora Atomic Host, System Security Services Daemon (SSSD) can be run on Fedora Atomic in spite of not being installed on Fedora Atomic OSTree (host image) by default.
The container image contains tools that are able to IPA-enroll the Atomic Host or join it to Active Directory, using
In the following, we'll assume the machine was IPA-enrolled and theatomic#atomic install fedora/sssd [...]
sssd service is enabled and running:
atomic#systemctl enable sssdCreated symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sssd.service to /etc/systemd/system/sssd.service. Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.wants/sssd.service to /etc/systemd/system/sssd.service.atomic#systemctl start sssd
With this setup, users defined in IPA server can log in to the
Atomic machine, provided host-based access control (HBAC) allows
the access. So user bob can log in via SSH,
either using password authentication (provided
PasswordAuthentication is set to
yes in /etc/ssh/sshd_config)
or for example using Kerberos/GSS-API:
We seeother-host$kinit bobPassword for bob@EXAMPLE.COM:other-host$ssh bob@atomic.example.comCould not chdir to home directory /home/bob: No such file or directoryatomic$iduid=1215800001(bob) gid=1215800001(bob) groups=1215800001(bob),1215800003(atomic-admins) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023atomic$hostnameatomic.example.com
bob is logged in, even if the account
is not listed in /etc/passwd —
SSSD in the container resolves the user identity and assisted
with the authentication and authorization.
Atomic admins
Let's assume bob should be able to execute
some basic administration tasks on the Atomic machine, without
having full root access. However, attempts
to run docker or atomic
are likely to fail:
atomic$docker psCannot connect to the Docker daemon. Is the docker daemon running on this host?atomic$atomic host status/usr/bin/atomic needs to be run as root.
Command
sudo is typically used to grant access
to run processes with elevated privileges, for example as
root. Configuration and access definition
is stored in /etc/sudoers and
/etc/sudoers.d ... but it can also come
from IPA server via SSSD. With the steps below we will
configure Sudo Rule in IPA so that bob and
every other user in atomic-admins user
group can run some basic docker and
atomic commands.
With the id above we've already verified that
bob is member of atomic-admins.
We can also list the user group membership on the IPA server:
Alternatively, IPA WebUI can provide the information, in → → :ipa$ipa group-find atomic-admins--------------- 1 group matched --------------- Group name: atomic-admins GID: 1215800003 Member users: alice, bob, david ---------------------------- Number of entries returned 1 ----------------------------
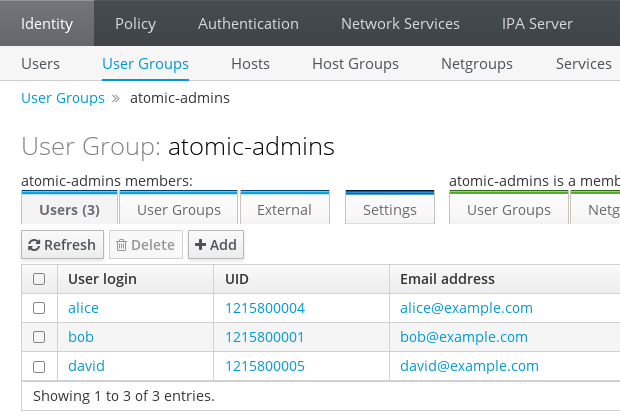
If we need to add additional user to the group, we can use ipa group-add-member on command line or add the user via the button on IPA WebUI.
Sudo Commands
To make subsequent manipulation easier, we will define Sudo Commands in IPA and group them in Sudo Command Group. We can achieve that on WebUI, → → and → → .
Alternatively, the commands and groups can be defined on command line:
ipa$ipa sudocmdgroup-add atomic-admin-read-------------------------------------------- Added Sudo Command Group "atomic-admin-read" -------------------------------------------- Sudo Command Group: atomic-admin-readipa$for i in '/bin/docker ps' '/bin/docker ps -a' '/usr/bin/atomic host status' ; do>ipa sudocmd-add "$i">ipa sudocmdgroup-add-member --sudocmds="$i" atomic-admin-read>done----------------------------------- Added Sudo Command "/bin/docker ps" ----------------------------------- Sudo Command: /bin/docker ps Sudo Command Group: atomic-admin-read Member Sudo commands: /bin/docker ps ------------------------- Number of members added 1 ------------------------- -------------------------------------- Added Sudo Command "/bin/docker ps -a" -------------------------------------- Sudo Command: /bin/docker ps -a Sudo Command Group: atomic-admin-read Member Sudo commands: /bin/docker ps, /bin/docker ps -a ------------------------- Number of members added 1 ------------------------- ------------------------------------------------ Added Sudo Command "/usr/bin/atomic host status" ------------------------------------------------ Sudo Command: /usr/bin/atomic host status Sudo Command Group: atomic-admin-read Member Sudo commands: /bin/docker ps, /bin/docker ps -a, /usr/bin/atomic host status ------------------------- Number of members added 1 -------------------------
We can check the result on command line
or on WebUI:ipa$ipa sudocmdgroup-find atomic-admin-read---------------------------- 1 Sudo Command Group matched ---------------------------- Sudo Command Group: atomic-admin-read Member Sudo commands: /bin/docker ps, /bin/docker ps -a, /usr/bin/atomic host status ---------------------------- Number of entries returned 1 ----------------------------
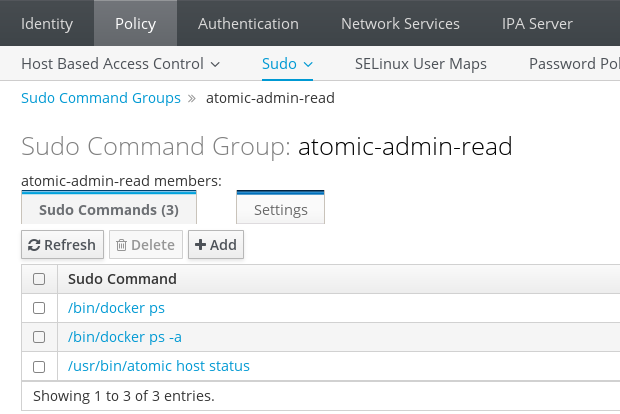
Sudo Rule
Now it's time to define Sudo Rule which will link the user group
atomic-admins to the Sudo Command Group
atomic-admin-read we've created above.
Our requirement for the rule are:
- every user member of
atomic-adminshas to be able to execute the commands; - on every machine;
- the commands will be executed as
root; - the users should not have to enter their password.
bob should be able to execute
and should get list of running containers.atomic$sudo docker ps
On IPA server's command line, the steps would include:
Theipa$ipa sudorule-add --hostcat=all atomic-admin-read----------------------------------- Added Sudo Rule "atomic-admin-read" ----------------------------------- Rule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: allipa$ipa sudorule-add-user --groups=atomic-admins atomic-admin-readRule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: all User Groups: atomic-admins ------------------------- Number of members added 1 -------------------------ipa$ipa sudorule-add-allow-command --sudocmdgroups=atomic-admin-read atomic-admin-readRule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: all User Groups: atomic-admins Sudo Allow Command Groups: atomic-admin-read ------------------------- Number of members added 1 -------------------------ipa$ipa sudorule-add-runasuser --users=root atomic-admin-readRule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: all User Groups: atomic-admins Sudo Allow Command Groups: atomic-admin-read RunAs External User: root ------------------------- Number of members added 1 -------------------------ipa$ipa sudorule-add-option --sudooption='!authenticate' atomic-admin-read------------------------------------------------------------- Added option "!authenticate" to Sudo Rule "atomic-admin-read" ------------------------------------------------------------- Rule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: all RunAs External User: root Sudo Option: !authenticate
!authenticate option causes password-less
execution, like NOPASSWD in
/etc/sudoers* would.
Let us check the resulting Sudo Rule:
ipa$ipa sudorule-find atomic-admin-read------------------- 1 Sudo Rule matched ------------------- Rule name: atomic-admin-read Enabled: TRUE Host category: all User Groups: atomic-admins Sudo Allow Command Groups: atomic-admin-read RunAs External User: root Sudo Option: !authenticate ---------------------------- Number of entries returned 1 ----------------------------
Of course, we could have created the setup on the WebUI as well,
under → → and , atomic-admin-read and .
We can also check the result on the WebUI:
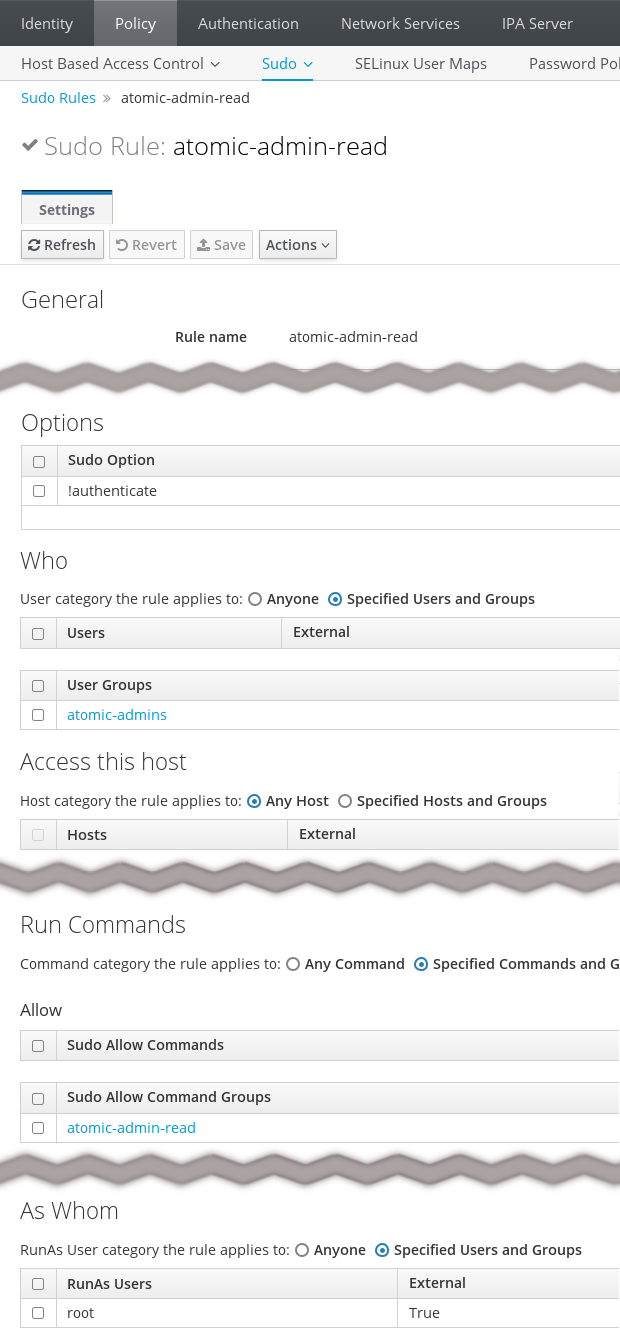
Using sudo
Now it's time to test the new Sudo Rule. With SSSD running in
container on Atomic Host and logged in as bob,
commands listed in the Sudo Command Group should work when
passed to sudo:
We can see the the command that used to fail when run directly because the user did not have access to the Unix socket used by docker daemon now passes. So will pass the other two commands specified in the Sudo Command Group.atomic$sudo docker psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 5e464ff2c527 fedora/sssd "/bin/run.sh" About an hour ago Up 10 minutes sssd
We've shown a simple example of defining Sudo Rule in IPA server and using it on Fedora Atomic Host. Of course, in real-world setups the rules will likely be more complex, perhaps using host groups as well, and having different sets of commands for different categories of admin users. However, the principles will stay the same and Atomic will be able to consume the rules, looked up and resolved by SSSD.
Versions used
- Fedora 23.53 Atomic Host (ostree)
- SSSD container docker.io/fedora/sssd: 5e464ff2c527 (use
docker images)